Symptoms of high blood pressure
- dizziness and headache;
- Pulsating sensation in different parts of the body, such as the back of the head and temples;
- Feeling "woozy" and experiencing decreased vision;
- ringing in the ears and audible heartbeat;
- Insomnia, fatigue;
- loss of appetite and nausea;
- Pressure and pain in the chest;
- Shortness of breath at rest and during light physical activity;
- increased sweating;
- facial redness;
- Swelling of hands and face.
causes of high blood pressure
- Kidney and adrenal gland disease. The function of these organs plays an important role in the regulation of the cardiovascular system. Secondary hypertension can occur in the context of chronic pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, adrenal tumors, and other pathologies;
- Thyroid disease. This organ secretes hormones needed to regulate body functions;
- metabolic and hematologic diseases such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis;
- Chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- Genetic factors lead to cardiovascular system dysfunction;
- Pathologies of the female reproductive system are complicated by hormonal imbalances.
Get consultation
Why choose a professional clinic?
- Treatment is according to clinical guidelines
- Comprehensive assessment of disease nature and treatment prognosis
- Modern diagnostic equipment and our own laboratory
- High level of service and balanced pricing policy
Hypertension diagnosis in modern clinics
- Dynamic blood pressure measurement can rule out situational (natural) hypertension. Doctors measure blood pressure in a quiet environment. You must avoid physical activity, smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking certain medications before taking this test. The cardiologist placed a tonometer cuff 2. 5 cm above the elbow and measured pressure in both arms. For convenience, the patient can be positioned lying down or standing. The study is conducted every 2-5 minutes to obtain multiple indicators and determine average blood pressure levels;
- General and biochemical blood tests. Cardiologists refer patients to the study to test for factors in high blood pressure. In the treatment room, the nurse treats the patient's antecubital fossa with antiseptic, squeezes the patient's shoulder area with a tourniquet, and draws blood with a syringe. In the laboratory, experts measure blood samples for levels of lipids, creatinine, hormones, glucose and potassium. The ratio and number of blood cells were also determined;
- Urinalysis. The doctor explains to the patient how and when it is necessary to fill the sterile container with urine. Laboratory urine testing allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of kidney filtration and identify inflammatory diseases of the excretory system;
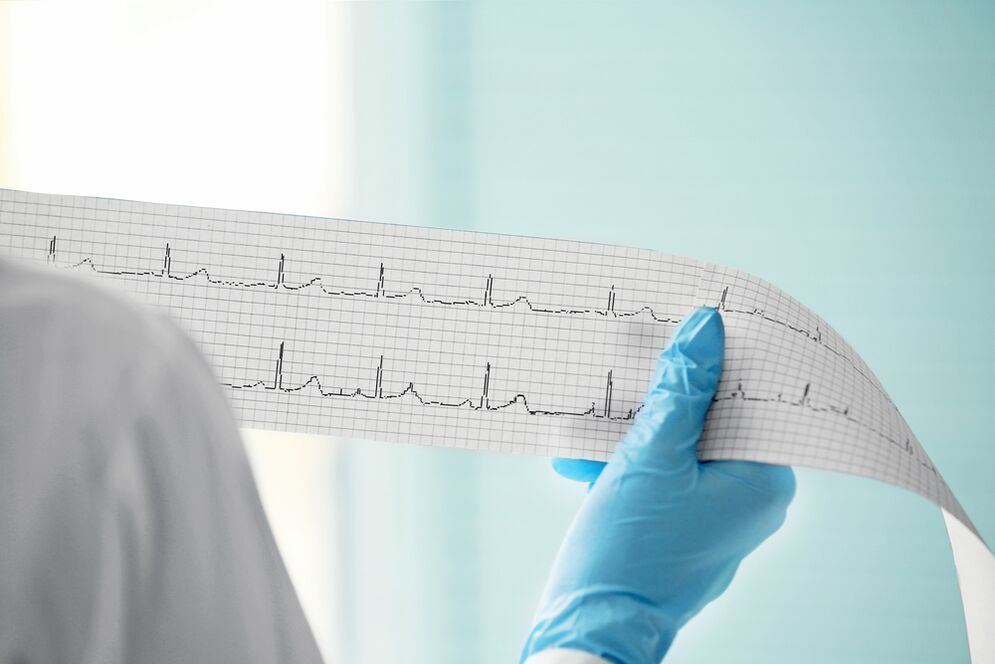
- An electrocardiogram is the study of the electrical activity of the heart and can allow people to discover the causes and signs of disease. During the procedure, doctors ask the patient to lie on his back and attach sensors (electrodes) to different parts of the body. The electrocardiogram is then collected and deciphered;
- Cardiac ultrasound is the safest way to examine the heart and can detect pathological changes in the organ, such as left ventricular wall thickening. Doctors have the patient lie on their back and press the sensor against the skin to obtain images of the heart on a monitor.
Treatment of high blood pressure
- Prescription of thiazide diuretics. These are diuretics, which stimulate the kidneys to remove more fluid from the body. Doctors prescribe these medications to reduce swelling and normalize blood pressure;
- Prescription of ACE inhibitors. These drugs are used to inhibit vasoconstrictors and lower blood pressure. Additionally, these medications are used to treat the underlying cause of high blood pressure related to kidney disease;
- Use an angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Cardiologists prescribe these drugs to inhibit the activity of vasoconstrictor factors;
- Use calcium channel blockers. These drugs lower blood pressure by relaxing the muscles in the walls of blood vessels and slowing the heart rate;
- Use alpha and beta blockers. If necessary, cardiologists prescribe these drugs to lower the heart rate, ease the load on the heart, and dilate blood vessels;
- Use an aldosterone antagonist. The main effect of these drugs is to improve kidney function, manifested by increased fluid and salt secretion. Due to this effect, blood pressure can be lowered;
- Administer additional medical therapy, including renin inhibitors, lipid-lowering agents, sedatives, and vasodilators.
Prevent high blood pressure
- Improve your diet, including avoiding greasy, salty and fried foods;
- quit drinking and smoking;
- Lose weight and engage in regular physical activity;
- Prompt treatment of diseases of the kidneys and endocrine organs.